An echocardiogram is a test that uses sound waves to create pictures of the heart. It is used with children to help diagnose defects of the heart that are present at birth (congenital). The picture is more detailed than a regular x-ray image. An echocardiogram also does not expose children to radiation.
Your child's health care provider may do the test in a clinic, in a hospital, or at an outpatient center. Echocardiography in children is done either with the child lying down or lying in their parent's lap. This approach can help comfort them and keep them still.
For each of these tests, a trained sonographer performs the test. A cardiologist interprets the results.
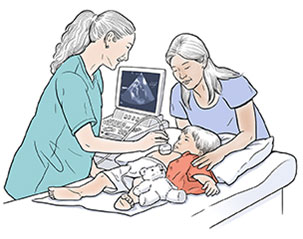
TTE is the type of echocardiogram that most children will have.
The test allows the provider to see the heart beating. It also shows the heart valves and other structures.
Sometimes, the lungs, ribs, or body tissues may prevent the sound waves from producing a clear picture of the heart. In this case, the sonographer may inject a small amount of liquid (contrast dye) through an IV to better see the inside of the heart.
TEE is another type of echocardiogram that children can have. The test is done with the child lying under sedation.
This test is done to examine the function, heart valves, major blood vessels, and chambers of a child's heart from outside of the body.
Your child may have an increased risk for heart problems due to an abnormal genetic test or other birth defects that are present.
The provider may recommend a TEE if: